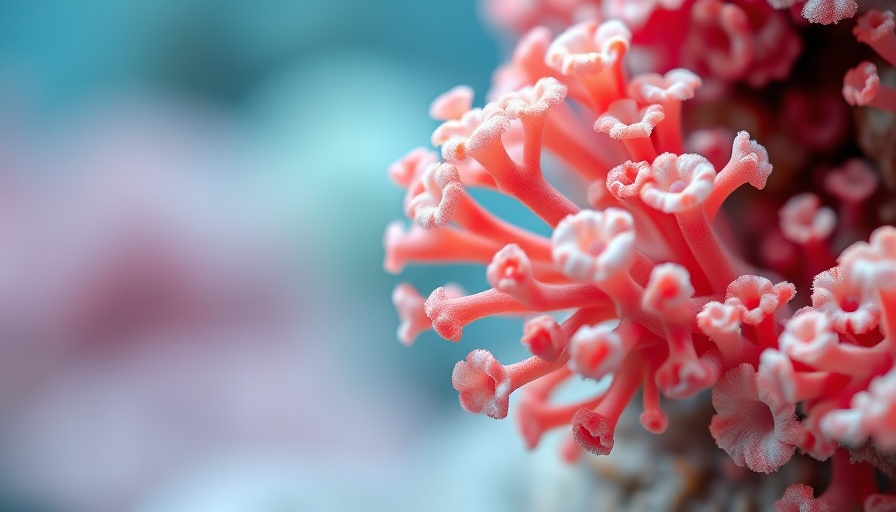
Unlocking Marine Secrets: The Anti-Cancer Potential of Soft Corals
Researchers from the University of California - San Diego have made a groundbreaking discovery regarding soft corals, revealing their potential to produce powerful chemical compounds known as diterpenoids, which exhibit both anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. This innovative study leads the way for further exploration into the biomedical applications of marine life, a frontier that remains largely uncharted.
Understanding Diterpenoids: Nature’s Chemical Defenders
Diterpenoids are organic compounds often produced by plants and marine organisms as a form of defense against predators. Similar to how certain plants utilize these compounds to deter herbivores, octocorals appear to engage in this strategy, providing them with a unique evolutionary advantage. Previous challenges in studying these compounds stemmed from their limited availability; traditional extraction methods from marine organisms are not only costly but also environmentally destructive.
The Breakthrough: Genetic Blueprint for Diterpenoid Production
The recent findings published in Nature Chemical Biology outline the discovery of a gene cluster responsible for the synthesis of diterpenoids in octocorals. This crucial genetic information indicates that it’s now possible to replicate these compounds in a laboratory setting, addressing the problem of supply for future drug development. As Bradley Moore, the study’s senior author, states, “With the genetic blueprint for producing these chemicals now in hand, the door is open to discover new compounds that could benefit humankind.”
Equal Footing: Marine vs. Terrestrial Drug Sources
Historically, around half of all medicinal drugs have derived from terrestrial plants. Despite covering an impressive 70% of the Earth’s surface, the ocean has been relatively under-researched compared to land. The study highlights the necessity for increased focus on marine sources, potentially expanding the variety of treatments available for complex conditions such as cancer and chronic inflammation.
Future Implications: What Lies Ahead?
The future of biotechnological innovation is ripe with possibilities as we venture deeper into the oceans. This study not only opens doors for medical researchers but also emphasizes the importance of preserving marine ecosystems. As these environments face increasing threats from climate change and human activity, safeguarding our oceans becomes crucial—not only for biodiversity but also for human health advancements.
Conclusion: Join the Conversation
This research illustrates the intersection of marine biology and biotechnology, paving the way for sustainable medical solutions. As the scientific community delves into the ocean's depths for answers, we encourage everyone to engage with these findings and promote ocean conservation. After all, what we learn from the sea could one day lead to revolutionary breakthroughs in medicine.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment