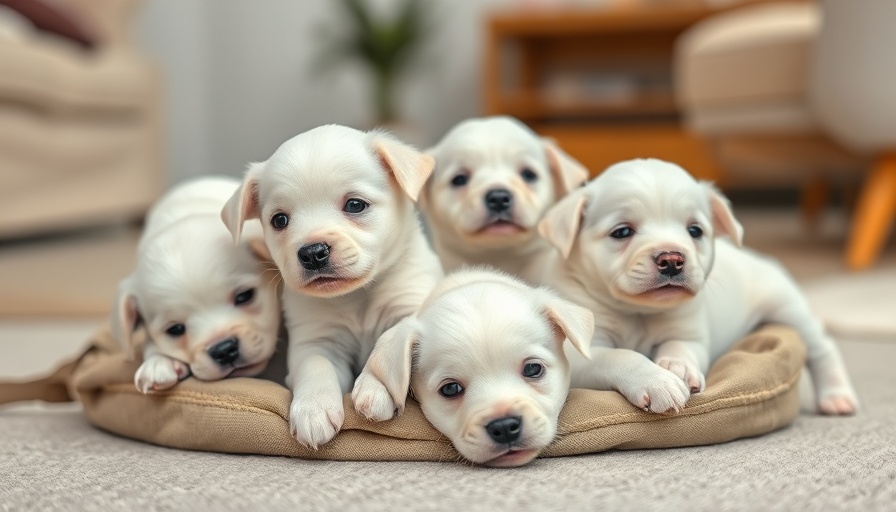

The Birth of a New Era in Genetic Engineering
In a groundbreaking revelation from the Dallas-based biotech company Colossal, three pups named Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi have captured the imagination of many. These aren't just any puppies; they carry the DNA of the long-extinct dire wolf, a majestic predator that roamed North America over 10,000 years ago. However, it’s essential to clarify that this isn’t a tale of revival akin to science fiction, but rather a remarkable feat of genetic engineering that highlights advancements in synthetic biology.
Modern Techniques in Action
Colossal’s method involved a meticulous process of extracting ancient DNA from fossilized remains, which included a 13,000-year-old tooth and a 72,000-year-old ear bone. Scientists sequenced this ancient genome and compared it with that of contemporary gray wolves, identifying approximately 20 genetic differences that distinguish the dire wolf from its modern relatives. Through CRISPR-Cas9, a powerful gene-editing tool, these specific traits were precisely edited into the genome of a gray wolf.
Questioning the Nature of 'Resurrection'
The narrative surrounding these revitalized pups often invites awe, framing it within the context of a 'resurrection.' However, that premise warrants scrutiny. What does it truly mean to 'bring back' an extinct species? The current pigs of Romulus, Remus, and Khaleesi are, in essence, wolves enriched with selective traits from an ancient lineage. They represent an exciting glimpse into the potential future of genetic engineering while simultaneously reminding us of the limitations that frame this scientific achievement.
Implications for Conservation and Ethics
This pioneering work asks critical questions about the ethics of genetic manipulation and its implications for conservation. As scientists venture into resurrecting species, one cannot help but reflect on the broader impact such advancements might hold for contemporary biodiversity. Will the drive to engineer DNA overshadow crucial conservation efforts aimed at protecting existing endangered species? The technology's dual-edged sword forces us to question our approach to nature, biodiversity, and bioethics.
A Look Forward: The Future of Genetic Engineering
As we stand on the cusp of potentially revolutionizing how we perceive extinction and conservation through technology, the Gene-editing ability showcased by the birth of these dire wolf pups serves as a testament to human ingenuity. Yet, it also comes with a heavy responsibility. The promise of synthetic biology opens new avenues not only for species engineering but also for addressing ecological crises facing our planet today. Can we align this powerful technology with the nature of ethics and sustainability?
As we reflect on these revolutionary advancements, it is crucial to remain engaged with the conversations surrounding biotech developments. Understanding the implications of such technologies on both a local and global scale is our collective responsibility.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment