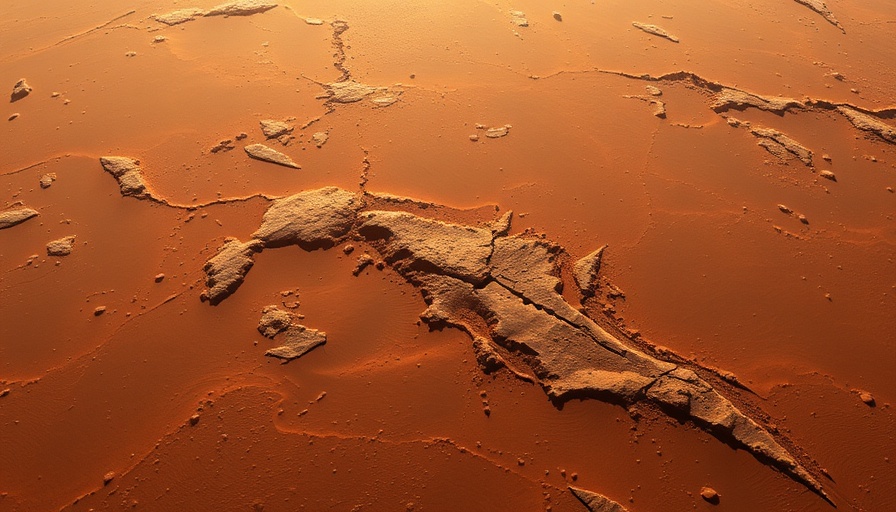

Is Mars Really Red? Unpacking the Myth
From ancient civilizations gazing up at the night sky to modern space exploration, Mars has captured the imagination of people worldwide. Often referred to as the 'red planet,' its distinct reddish hue has led to various interpretations and meanings across cultures. However, the truth about its color is rooted in fascinating astrophysics and geological processes.
The Science Behind Mars' Color
The iconic red appearance of Mars primarily stems from iron oxide, commonly known as rust, that coats the planet’s surface. Much like our own blood derives its color from iron, the surface of Mars reflects light in a way that gives it a reddish impression when observed from Earth. Yet, when viewed closely, spacecraft have discovered a spectrum of colors, from rusty browns to tan shades, revealing a more intricate palette than the simple 'red' label implies.
Variations in Martian Surface Color
Beyond its reddish regions, Mars presents a diverse topography, including polar ice caps that appear white due to frozen water and carbon dioxide. These ice caps fluctuate with changing seasons, showcasing how dynamic the Martian environment can be. Observations from rovers and orbiters over the decades highlight that the red coloration is not uniform. For instance, images from the Viking lander in 1976 marked the first glimpse of a dusty Martian landscape, providing evidence of the planet's geological complexity.
Perception Through Different Telescopes
One intriguing aspect of seeing Mars is how it's perceived through various telescopes. Telescopic technology has progressed remarkably, granting scientists the ability to capture wavelengths beyond visible light. Through advanced imaging techniques, astronomers are able to identify emissions from ultraviolet to infrared spectra, each revealing valuable information about the planet’s atmosphere and surface composition.
Future of Mars Exploration: A Technological Leap
With ongoing advancements in space innovation, our understanding of Mars is continuously evolving. For example, new missions equipped with sophisticated technology are set to explore its surface, atmosphere, and potential for past life. These missions not only seek answers about water presence but also the potential future of colonizing the planet. The implications of these explorations could redefine what we know about space and our very existence beyond Earth.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of Mars
As we deepen our exploration and understanding of Mars, the interplay of light, color, and geology will continue to reveal the intricacies of our neighboring planet. Whether it's through advanced telescopes or onsite rover exploration, each discovery brings us a step closer to answering profound questions about where humanity fits in the grand scheme of the universe.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment