Expanding Horizons in Crop Protection with Nature's Help
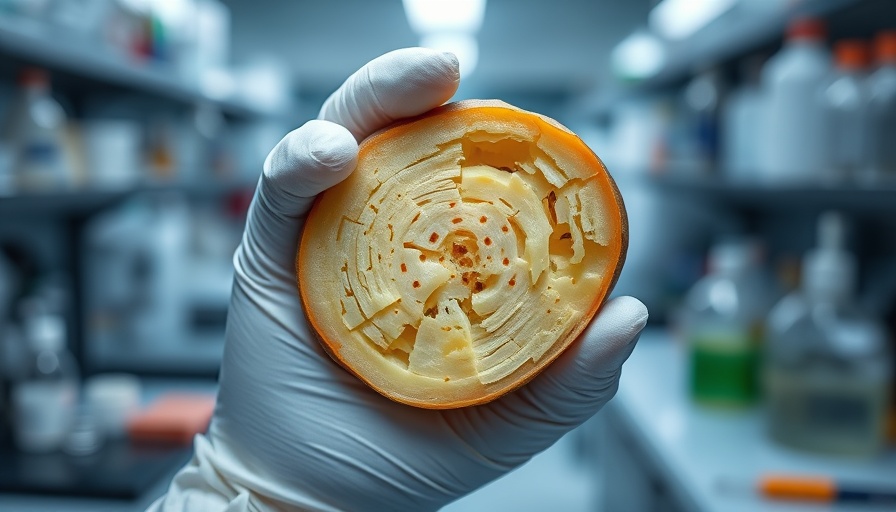
Innovation in agriculture is increasingly leaning towards utilizing natural solutions to combat crop diseases. A recent study from Texas A&M University highlights the potential of spinach antimicrobial peptides, specifically defensins, to protect key crops like citrus and potatoes from debilitating diseases.
Understanding the Threat: Citrus Greening and Potato Zebra Chip
Citrus greening disease, caused by the bacterium Candidatus Liberibacter spp., poses a significant threat to citrus production globally. Similarly, zebra chip disease affects potatoes, leading to substantial economic losses. Both diseases prompt farmers to seek new methods for maintaining crop health and productivity.
Spinach Defensins: Natural Heroes
Spinach defensins are naturally occurring proteins that play a crucial role in plant defense, providing robust resistance against a spectrum of pathogens. This quality makes them a prime candidate for sustainable agricultural practices. Texas A&M researchers have shown that these peptides can be effectively used to enhance the resilience of citrus and potato crops, promising to improve yield and crop quality while maintaining environmental safety.
A Safe Solution for Farmers and Consumers
Unlike many synthetic pesticides, spinach defensins have been deemed safe for consumption. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency concluded that dietary exposure to these peptides is safe, opening the door for their use in agriculture without raising health concerns among consumers, including vulnerable populations like infants and children.
Collaborative Efforts for Sustainable Agriculture
The research is a product of collaboration, notably involving the use of a benign virus developed by researchers from the University of Florida to deliver these peptides directly into commercial citrus trees. This innovative method signifies a promising step towards integrating biotechnology with traditional farming practices to foster sustainability and resilience in agriculture.
Future Implications and Opportunities for Farmers
With the ongoing challenges posed by crop diseases, the findings from this study offer a beacon of hope. Implementing spinach antimicrobial peptides could empower farmers to reclaim control over their crops, enhancing food security while aligning with sustainable agricultural practices. By focusing on eco-friendly methods, the agricultural sector can contribute to a healthier planet and a more resilient food system.
Join the Movement Towards Sustainable Farming!
The implications of spinach antimicrobial peptides extend beyond scientific discovery; they signal a shift towards a more conscientious approach to agriculture that respects both health and the environment. As consumers and advocates, we can support sustainable practices that help ensure a healthier planet for future generations. Let’s embrace these innovative solutions and explore ways to promote sustainable living!
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment