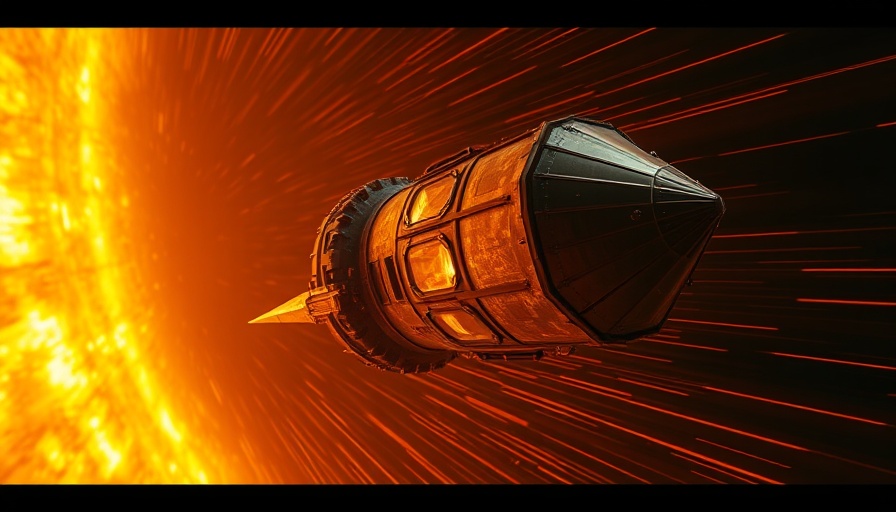

Exploring the Extraordinary: Varda's W-2 Mission
In a stunning display of engineering and innovation, the Varda Space capsule achieved a remarkable feat with its W-2 mission. Launched on January 16, 2024, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the capsule spent six successful weeks orbiting Earth, returning on February 27, 2024, to the Koonibba Test Range in South Australia. What makes this mission particularly intriguing is its potential impact on the burgeoning field of in-space manufacturing, where microgravity offers unique opportunities for production.
A Fiery Return to Earth
The video released by Varda brings viewers along for the exhilarating ride as the 265-pound capsule reenters Earth's atmosphere at remarkable speeds exceeding Mach 25. This high-velocity descent creates spectacular visuals as the capsule interacts with atmospheric layers, igniting sparks of various colors captured by onboard cameras. The immersive footage allows the audience to experience the thrill of reentry, typically reserved for astronauts and engineers.
The Significance of in-Space Manufacturing
Varda's mission isn't just about breathtaking videos; it's part of a larger vision for the future of manufacturing in space. CEO Will Bruey emphasizes that "removing gravity allows us to make medicines you otherwise couldn’t on Earth." The W-2 mission brought back a pharmaceutical reactor alongside a spectrometer from the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL), collecting crucial data to advance hypersonic technologies and in-space manufacturing. As Bruey puts it, changing the gravitational environment could revolutionize how medications are formulated and produced.
Previous Success and Future Potential
This mission follows the success of Varda's first mission, W-1, which landed in Utah, showcasing the significant progress Varda is making in this exciting sector. W-1 spent eight months in orbit and successfully returned space-grown crystals of the antiviral drug ritonavir, demonstrating the company’s innovative approach to drug development and manufacturing. With the rapid evolution of technology in the aerospace sector, Varda aims to establish itself as a leader in the in-space economy.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While Varda’s achievements are promising, the road to commercial viability in space manufacturing is fraught with challenges, including high costs, regulatory hurdles, and the need for technological advancements. However, as more companies invest in space exploration, we might see an ecosystem where the advantages of microgravity translate into real-world applications, particularly in healthcare and materials science.
Community Impact: What This Means for Us
The implications of Varda's missions extend beyond scientific curiosity; they could eventually influence how drugs are produced, enhancing manufacturing efficiency and potentially lowering costs. Future generations may benefit from medications designed in microgravity, highlighting why space exploration remains vital for societal advancement.
The success of Varda's missions underscores a key point: the future of space innovation is bright, and with continued investment and research, we could soon witness the rise of a new manufacturing frontier in space.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment