
Celebrating 35 Years of Cosmic Observations
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) marks a milestone that few human inventions achieve; it stands proudly at 35 years of extraordinary service to astronomy. Launched on April 24, 1990, aboard the space shuttle Discovery, HST was designed to provide groundbreaking views of the universe, unobstructed by Earth’s atmospheric distortion. Today, as we celebrate its anniversary, the wealth of knowledge gained from HST's nearly 1.7 million observations continues to inspire awe and innovation within the scientific community.
The Power of Hubble: Transforming Our View of Space
Over the years, HST has contributed to over 22,000 scientific papers and amassed approximately 400 terabytes of data. The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA, which jointly operate Hubble, note that before its launch, no generation had experienced the ability to view the cosmos in such vibrant detail. The latest release of images not only serves as a celebration of Hubble’s legacy but also highlights some of the most fascinating astronomical phenomena, particularly as recent snapshots reveal breathtaking views of Mars and a dying star architecting a stunning celestial formation.
Marvels of Mars: Seasonal Changes Unveiled
HST's latest images of Mars provide a glimpse into the planet's dynamic environment. Captured during Mars's winter months, these snapshots show ethereal water-ice clouds cloaking the Martian surface while highlighting seasonal transformations. As spring approaches in the northern hemisphere, carbon dioxide freezes, creating a thick layer of ice on the poles, which gradually sublimates, revealing the planet's rugged topography.
These visuals showcase iconic geographical features such as Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano in the solar system, alongside the geologically rich Tharsis Plateau. HST's remarkable ability to capture such detailed images significantly enhances our understanding of planetary science and climate dynamics beyond Earth.
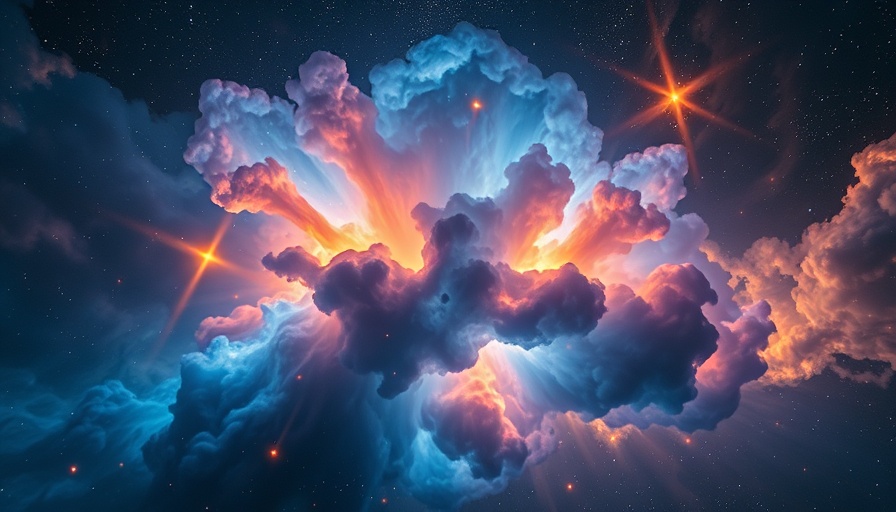
The Celestial Moth: A Nebula's Story
Beyond Mars, one of the most enchanting visuals released is that of NGC 2899—a planetary nebula emitting light in striking hues, reminiscent of a moth in flight. Located approximately 4,500 light-years away, this nebula serves as a fine example of stellar evolution. Powerful winds and intense radiation from a dying star create a beautiful yet intricate shape that captures the imagination of astronomers and stargazers alike.
HST's ability to unveil such complexities in celestial formations provides insight into the life cycles of stars, profoundly influencing our understanding of the universe's past, present, and future.
The Legacy of Curiosity and Innovation
The Hubble Space Telescope stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Its legacy challenges us to think beyond our planet and explore the vast expanse of space. As scientists and enthusiasts alike look back at HST's achievements, the mission remains as relevant today as it was three and a half decades ago.
As we gaze into the cosmos, we are reminded of HST's role in bridging the gap between our immediate understanding and the myriad wonders that lie beyond our reach. Each photograph taken by HST is not merely an image, but a beacon of curiosity that inspires future innovations in space exploration.
Conclusion
From understanding distant planets like Mars to observing dying stars sculpting their surroundings, the contributions of the Hubble Space Telescope continue to enrich our knowledge of the universe. As we look forward to the next era of exploration, let us reflect on the invaluable data HST has provided and consider how this knowledge shapes our future in tech and science.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment