Revolutionizing Health: The Dual-Action Peptide Discovery
In a time when the world is increasingly focused on health and recovery in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers are striving to develop innovative therapies that not only combat viruses but also aid in recovery. A recent breakthrough from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology has revealed an exciting new peptide, Ac-Tβ1-17, which shows promise as both an antiviral agent and a tissue repair enhancer. This fascinating development opens the door to a new era of therapeutic options derived from natural sources and peptide metabolites.
Understanding Peptides and Their Potential
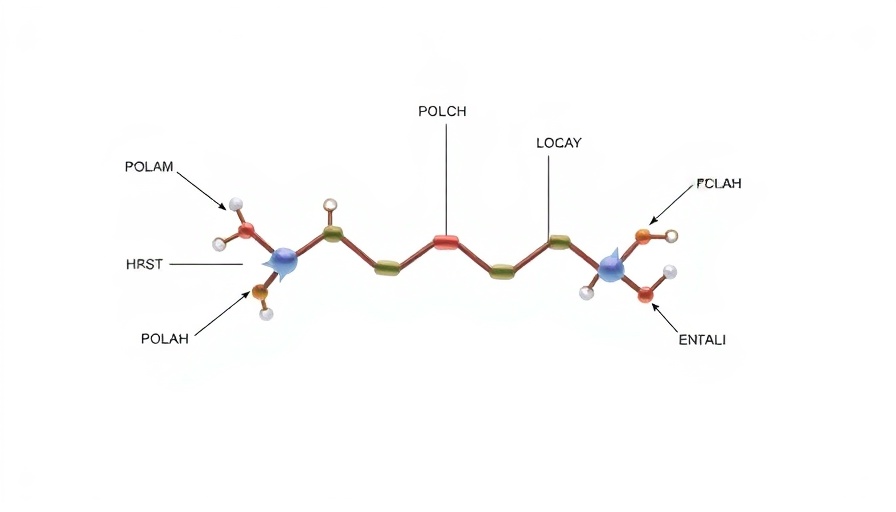
Peptides are small chains of amino acids that play crucial roles in biological processes. With a surge in interest regarding peptide-based drugs, notably after the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers are exploring their multifunctional roles in health and medicine. The peptide Ac-Tβ1-17, identified by a research team led by Dr. Hyung-Seop Han, demonstrates potent antiviral characteristics by inhibiting the COVID-19 virus protease, Mpro, by over 85%. This dual capability suggests peptides could pave the way for more efficient treatments against viral infections.
The Science Behind Ac-Tβ1-17
Ac-Tβ1-17 originates from thymosin β4, a natural protein that helps to regulate various cellular functions. Laboratory experiments showed that this peptide not only combats viral activities but also promotes vital recovery processes such as cell growth and wound healing. Furthermore, it encourages blood vessel formation and detoxification of reactive oxygen species, which can damage tissues. This comprehensive effect enhances its appeal as a multifunctional therapeutic approach.
The Role of Scaffolds in Regenerative Medicine
A unique aspect of this research involves creating a peptide scaffold, which acts as a supportive structure for cells in healing tissues. The study found that this scaffold promotes effective tissue recovery, emphasizing the peptide's dual action in supporting both antiviral functions and tissue regeneration. Dr. Song, a member of the research team, highlighted that this innovation may tackle the limitations of traditional protein-based therapies, advancing regenerative medicine significantly.
Future Outlook: Customizing Therapeutics and Biomaterials
The implications of Ac-Tβ1-17 are vast. The research team's continued efforts will explore practical applications of the peptide in developing customized therapeutics and regenerative biomaterials. This could revolutionize how we address not just viral infections but also broader challenges in tissue repair and regeneration that many people face.
Summing Up
The discovery of Ac-Tβ1-17 exemplifies the exciting possibilities within biological and biotechnological advancements. By focusing on natural peptide metabolites, researchers are opening avenues that could lead to significant improvements in clinical treatments. With real-world applications on the horizon, the future of health interventions looks promising.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment