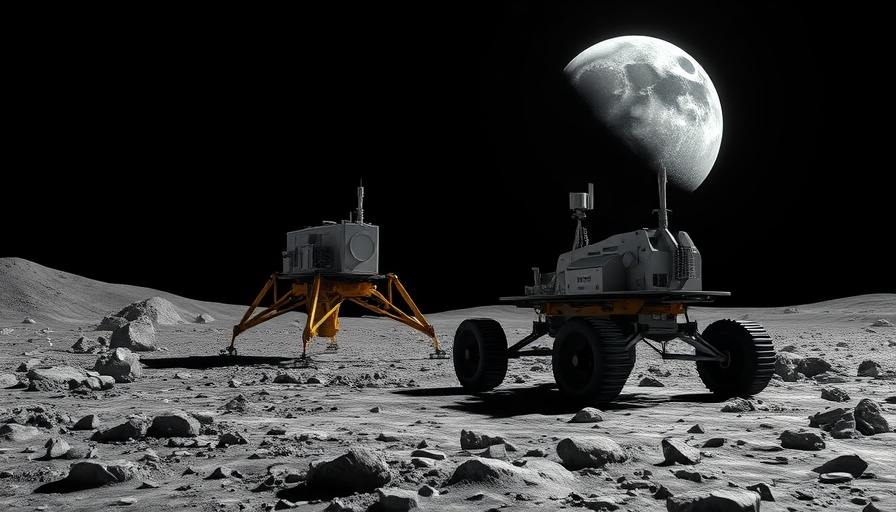

The Historic Landing of ispace's Resilience Probe
On June 5, 2025, Japan's private space company ispace will attempt to achieve a milestone in lunar exploration with its Resilience lander, aiming to become one of the first private companies to successfully land on the moon. Scheduled for landing at 3:24 p.m. EDT (1824 GMT)—equivalent to 4:24 a.m. Japan Standard Time on June 6—the event marks a critical redemption mission following ispace's earlier unsuccessful attempt with the Hakuto-R Mission 1.
Why This Mission Matters
The quest for lunar exploration is not just about national pride; it symbolizes the potential for innovation and investment in private aerospace endeavors. Given the surge of interest in moon missions from both governmental and private sectors—including NASA’s Artemis program—this mission represents an exciting phase in the evolution of space exploration.
How Will You Watch the Landing?
For those eager to witness this event, ispace will provide a live stream of the landing via its official YouTube channel, beginning coverage at 2:10 p.m. EDT (1810 GMT). Viewers can choose from broadcasts in Japanese with English translations available, thereby making the event accessible to a global audience.
Prepared for Contingencies
While the targeted landing spot is within Mare Frigoris, the Sea of Cold, ispace has prepared alternative landing sites should conditions demand a change in plans. This flexibility showcases the company’s commitment to safety and precision in space operations. The team has identified three backup sites, each with distinct landing dates and times.
Building Upon Past Experiences
This mission is more than just a standalone event; it’s part of ispace's larger journey in space exploration. Their earlier attempt highlighted both the challenges and opportunities present in the industry, including aspects of mission planning, execution, and technology development. The lessons learned from the Hakuto-R Mission 1 will undoubtedly inform strategies for Resilience, showcasing how past failures can lead to future successes in innovation.
What’s Next After the Landing?
If successful, the Resilience lander's achievement could pave the way for more complex missions involving lunar utilization and exploration. Future missions may include collaborations with international space agencies, potential commercial endeavors, and scientific investigations into the moon’s geology.
Seizing the Opportunity
This upcoming landing marks not only a significant technological achievement but also an opportunity for students and aspiring engineers to engage with the open world of space. The mission could inspire a new generation interested in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, essential for fostering innovation.
The success of ispace's Resilience mission could redefine the paths science and private industry can explore together on their journey to partner with government space agencies worldwide in the quest for space exploration and the advancement of human knowledge.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment